All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the International Myeloma Foundation or HealthTree for Multiple Myeloma.
The mm Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the mm Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The mm and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Multiple Myeloma Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, Legend Biotech, Pfizer, and Roche. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View multiple myeloma content recommended for you
In patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM), lenalidomide is the preferred choice for maintenance therapy after autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). Currently, there are limited data from phase III trials surrounding any alternatives to lenalidomide as a form of post-ASCT therapy.
Below, we summarize an interim analysis from the phase III, open-label, randomized ATLAS trial investigating carfilzomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone (KRd) versus lenalidomide alone (R) for the treatment of NDMM after ASCT, recently published in The Lancet Oncology by Dytfeld et al.
Study design
In total, 180 patients across 12 academic and clinical centers in the USA and Poland were randomized at a 1:1 ratio in block sizes of four and six to receive KRd or R. The study protocol is outlined in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Study protocol*
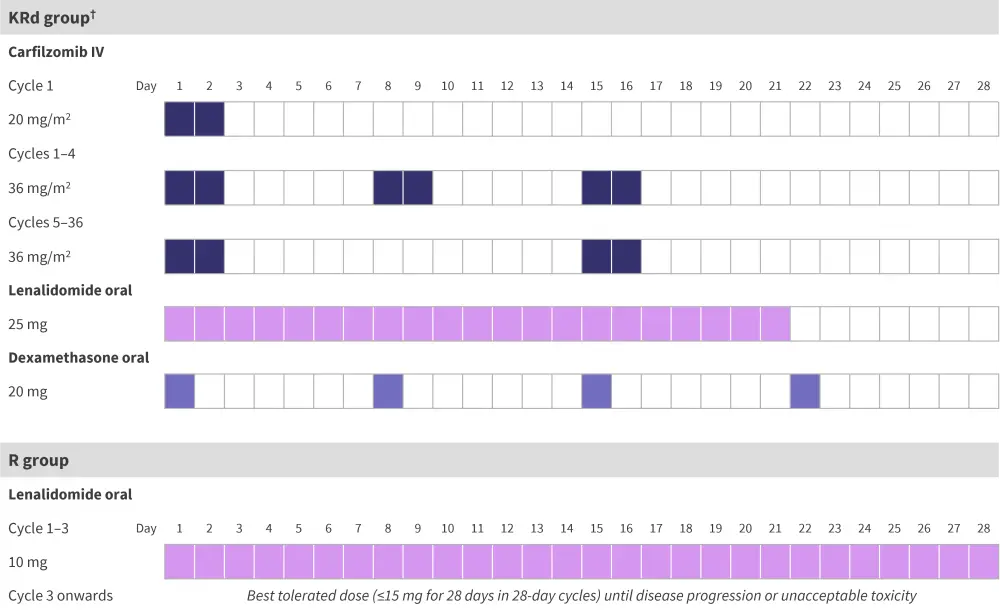
IV, intravenous; KRd, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone; MRD, measurable residual disease; R, lenalidomide monotherapy.
*Adapted from Dytfeld, et al.1
†Patients in the combination treatment group with no detectable MRD after Cycle 6 and standard risk cytogenetics were switched to R (best tolerated dose up to 15 mg) as of Cycle 9. This was done to limit toxic effects and financial burden on patients.
The eligibility criteria for enrolled patients are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Patient eligibility criteria*
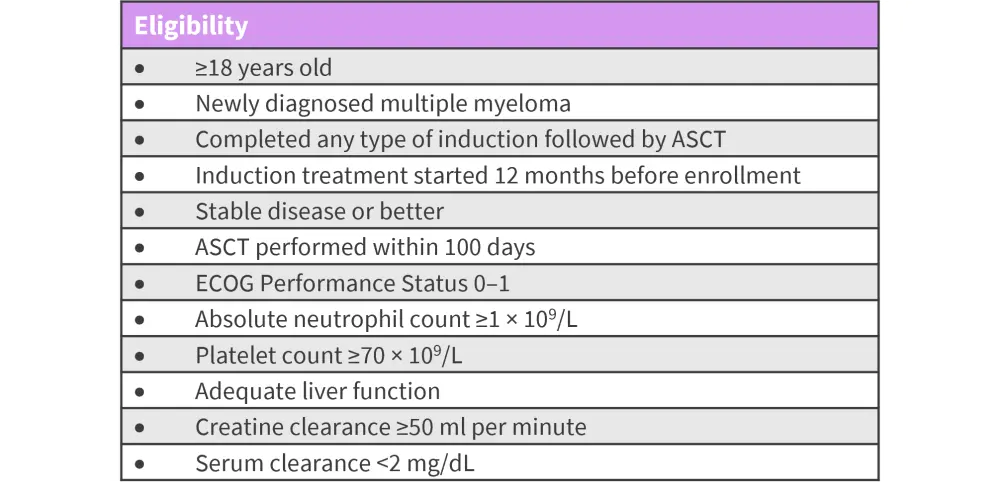
ASCT, autologous stem cell transplantation; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group;
*Adapted from Dytfeld, et al.1
Results
- The primary endpoint was progression free survival (PFS) from randomization to disease progression or death.
- Secondary endpoints included the rate of measurable residual disease (MRD) negativity at Months 6, 12, 18, 24, and 36, duration of MRD, depth of response, overall survival, and safety.
- The baseline patient characteristics were well balanced between the two treatment groups (Table 1).
Table 1. Baseline patient characteristics*
|
ASCT, autologous stem cell transplantation; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; ISS, |
||
|
Characteristic, % (unless otherwise stated) |
KRd (n = 93) |
R (n = 87) |
|---|---|---|
|
Median age, years |
57 |
59 |
|
Sex |
||
|
Female |
53 |
40 |
|
Male |
47 |
60 |
|
ECOG Performance Status, % |
||
|
0 |
49 |
38 |
|
1 |
51 |
62 |
|
ISS stage |
||
|
I |
42 |
32 |
|
II |
42 |
48 |
|
III |
16 |
20 |
|
Cytogenetic profile |
||
|
Standard risk |
77 |
79 |
|
High risk† |
23 |
21 |
|
Median time from ASCT, days |
92 |
98 |
|
Type of induction |
||
|
Bortezomib, thalidomide, and |
69 |
61 |
|
Bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and |
15 |
20 |
|
Other‡ |
16 |
20 |
|
Previous treatment |
||
|
Lenalidomide-containing regimen |
11 |
13 |
|
Carfilzomib-containing regimen |
4 |
6 |
|
Number of induction regimens |
||
|
1 |
92 |
94 |
|
2 |
8 |
6 |
Efficacy
After a median follow-up of 33.8 months,
- 41% of patients from the KRd group had discontinued treatment compared with 57% of patients in the R group;
- dose reductions occurred in 34% of patients in the KRd group and 40% of patients in the R group;
- after Cycle 8, 44% of patients in the KRd group had switched to the R group;
- PFS was higher in the KRd group compared with the R group (Table 2);
- patients with standard risk cytogenetics in the KRd group had a longer PFS vs patients with standard risk in the R group (median not reached vs 65.5 months); and
- overall survival was not significantly different between the two treatment groups (Table 2).
No significant difference in the depth of response was observed between the two groups.
- Improvement in depth of response at 6 months post-ASCT was observed in 54% of patients in the KRd group and 44% of patients in the R group (p = 0.18).
- A higher percentage of patients recorded a complete response or better in the KRd group compared with the R group (Figure 3).
- The rate of MRD negativity after 6 cycles was higher in patients in the KRd group compared with the R group (Figure 3).
- MRD was assessed by centralized next-generation sequencing; if this was unavailable, centralized and standardised multiparametric flow cytometry was used.
Table 2. Survival outcomes in the KRd and R patient groups*
|
KRd, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone; NR, not reached; OS, overall survival; PFS, |
|||
|
Outcome, months |
KRd |
R |
p value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Median PFS |
59.1 |
41.4 |
0.012 |
|
Median OS |
NR |
61.8 |
0.68 |
Figure 3. Response outcomes*
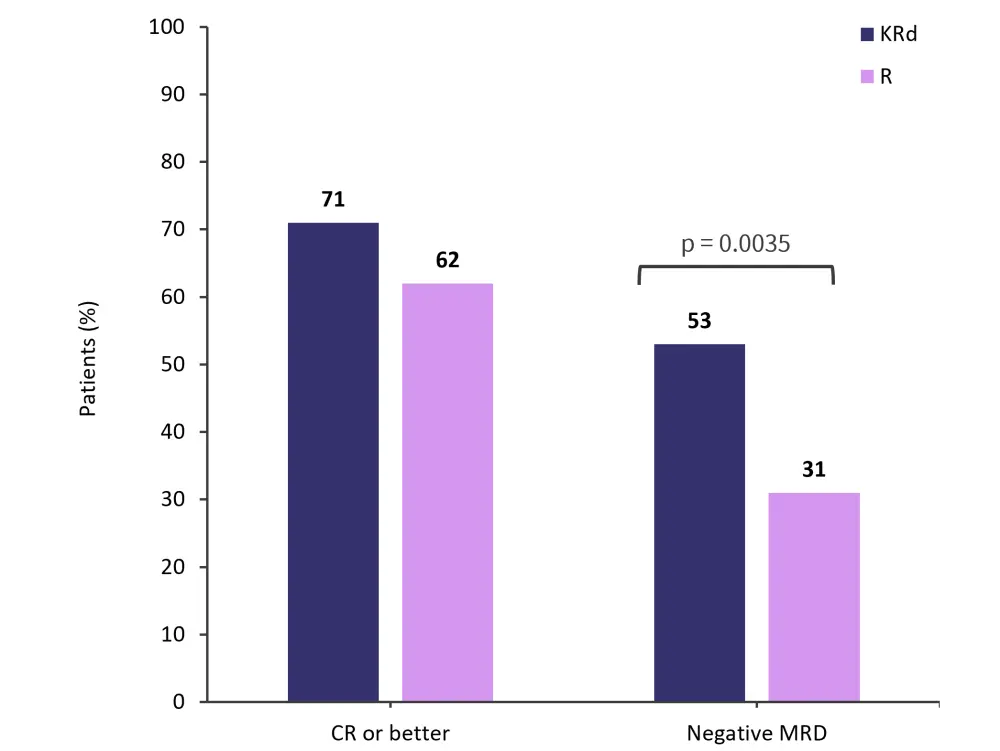
CR, complete response; MRD, measurable residual disease; KRd, carfilzomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone; R, lenalidomide monotherapy.
*Adapted from Dytfeld, et al.1
Safety
Grade 1/2 adverse events (AEs) were more common in the KRd group compared with the R group (93% and 83%, respectively).
- The most common Grade 1/2 hematologic AEs were thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, and anemia (Figure 4).
- The most common Grade 1/2 non-hematologic AEs were upper respiratory tract infection, fever, and aminotransferase increase (Figure 4).
Grade 3/4 AEs occurred in 76% and 73% of patients in the KRd and R group, respectively; these included neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and lower respiratory tract infection (Figure 5). AEs that led to treatment discontinuation were recorded in 4% of patients in the KRd group and 12% in the R group. Serious AEs were experienced by 28% of patients in the KRd group and 22% in the R group, the most common being lower respiratory tract infection (12% and 3%, respectively).
There was one treatment-related death, this was due to respiratory failure from pneumonia experienced by a patient in the KRd group. Two patients treated in the KRd group and one patient in the R group recorded secondary primary malignancies.
Figure 4. Most common Grade 1/2 hematologic and non-hematologic AEs in patients from the KRd and R groups combined*
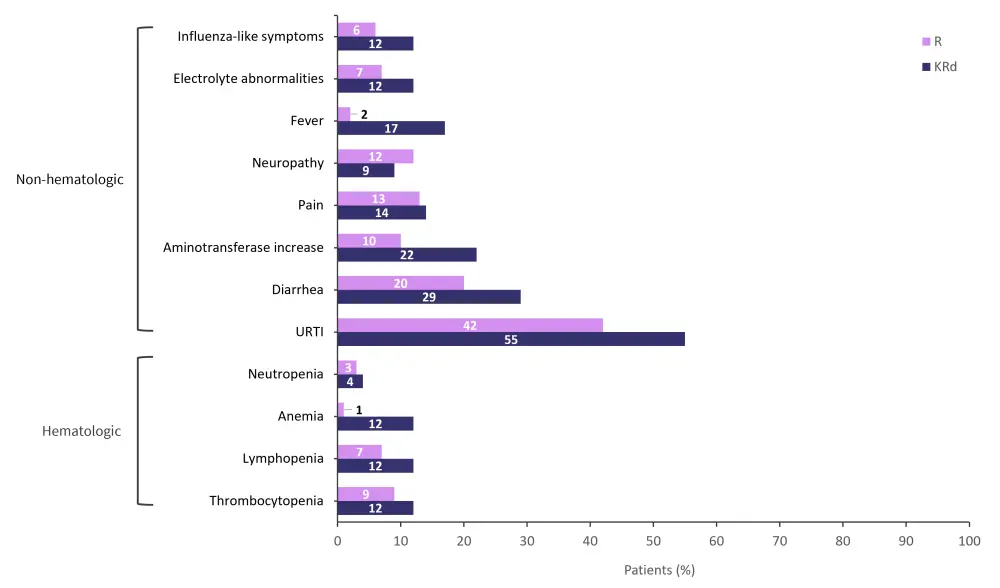
AE, adverse event; KRd, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone; R, lenalidomide monotherapy; URTI, upper respiratory tract infection.
*Adapted from Dytfeld, et al.1
Figure 5. Most common Grade 3/4 AEs in the KRd and R groups combined*
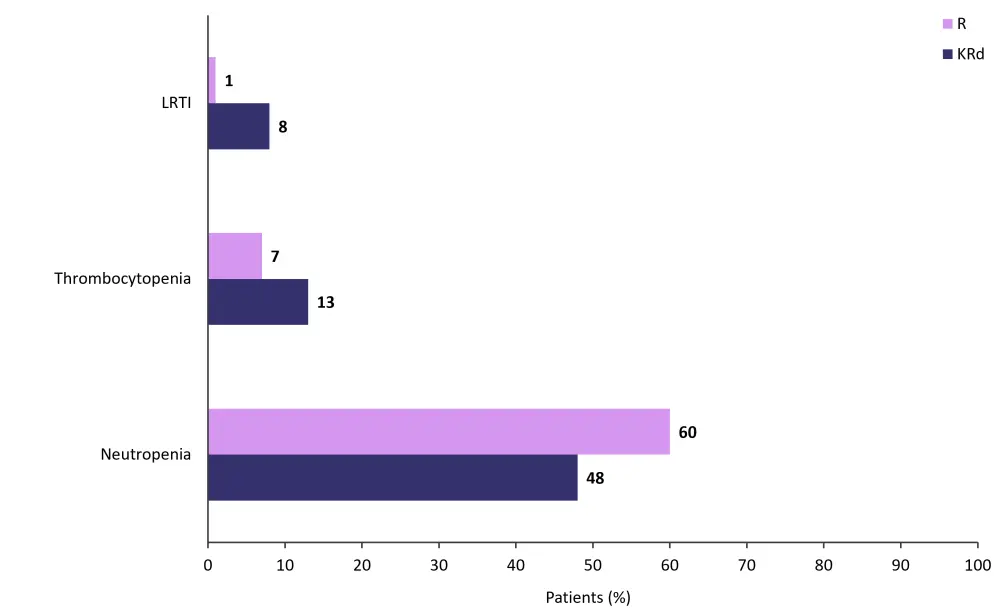
AE, adverse event; KRd, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone; LRTI, lower respiratory tract infection; R, lenalidomide monotherapy.
*Adapted from Dytfeld, et al.1
Conclusion
Overall, these findings outline the potential of KRd as a treatment for patients with NDMM. After 6 cycles of therapy, a higher percentage of patients achieved negative MRD-status and longer PFS in the combination group compared with lenalidomide-only treatment. The authors noted several limitations of this study, including the interim nature of the analysis and the low number of patients; although sufficient for the evalution of PFS, low patient numbers prevented statistical analysis among subgroups. Longer follow-up and MRD monitoring will further elucidate the efficacy of triplet-based maintenance and the safety of MRD-guided treatment reduction.
Expert Opinion
“The ATLAS study showed the superiority of KRd to standard lenalidomide maintenance in patients with multiple myeloma after bone marrow transplantation. The study was performed with close collaboration and supervision of Andrzej Jakubowiak from the University of Chicago but out of 180 patients, 159 were randomized and treated in Poland under the care of investigators from the Polish Myeloma Consortium.
The study showed for the first time in a randomized phase III trial that KRd is related to a 44% reduction in death and progression compared with lenalidomide alone. Patients treated with KRd had an 18-month longer PFS than those who received lenalidomide. The 3-drug regimen was not associated with significantly higher toxicity, which strongly argues for KRd to be a new standard of care in the maintenance setting.
The study also showed the efficacy of incorporating MRD-based treatment de-escalation. This modern approach is not often seen in phase III trials in myeloma and emphasizes the innovative nature of the ATLAS study. Moreover, its positive results could change the current standard of care in terms of using MRD-guided maintenance therapy utilizing KRd.”
 Dominik Dytfeld
Dominik DytfeldReferences
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content
Your opinion matters
On average, how many patients with MGUS/smoldering MM do you see in a month?




