All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the International Myeloma Foundation or HealthTree for Multiple Myeloma.
The mm Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the mm Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The mm and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Multiple Myeloma Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, Legend Biotech, Pfizer, and Roche. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View multiple myeloma content recommended for you
Do you know... Which of the following is NOT a current or future innovative solution to the common challenges facing CAR T-cell therapy?
Video series
During the EHA 2023 Hybrid Congress, the Lymphoma Hub and Multiple Myeloma Hub held a joint satellite session on the ins and outs of CAR T cells in the real world.
Here, we share the presentation by Michael Hudecek, University Hospital Würzburg, Würzburg, DE, discussing answers to common challenges in CAR T-cell therapy.
In this presentation, Hudecek identifies limitations in patient access and inefficient manufacturing protocols as the main challenges currently restricting the scalability of CAR T-cell therapies (Figure 1), before highlighting some possible innovative answers (Figure 2).
Figure 1. The effect of limited patient access on CAR T-cell therapy for patients with DLBCL in Italy*
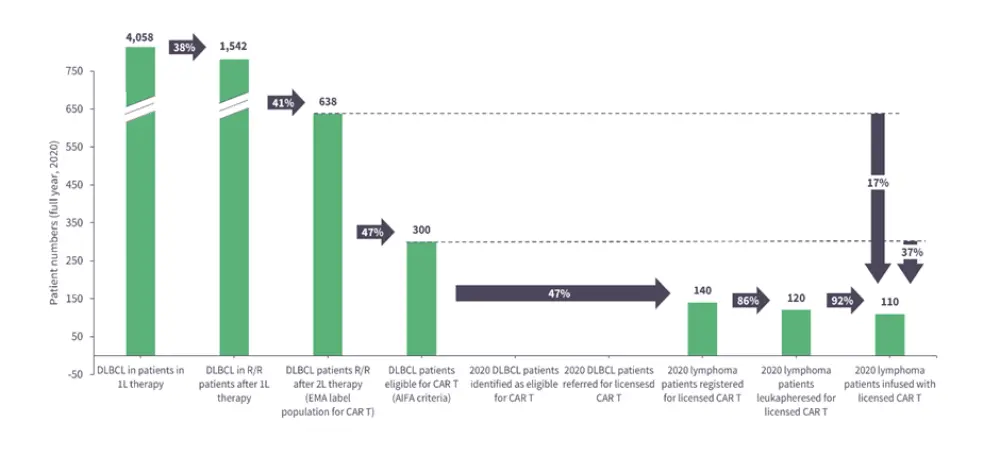
CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; R/R, relapsed/refractory;
2L, second line.
*Adapted from Jommi, et al.1
Figure 2. The impact of centralized CAR T-cell manufacturing on wait times for CAR T-cell infusion*
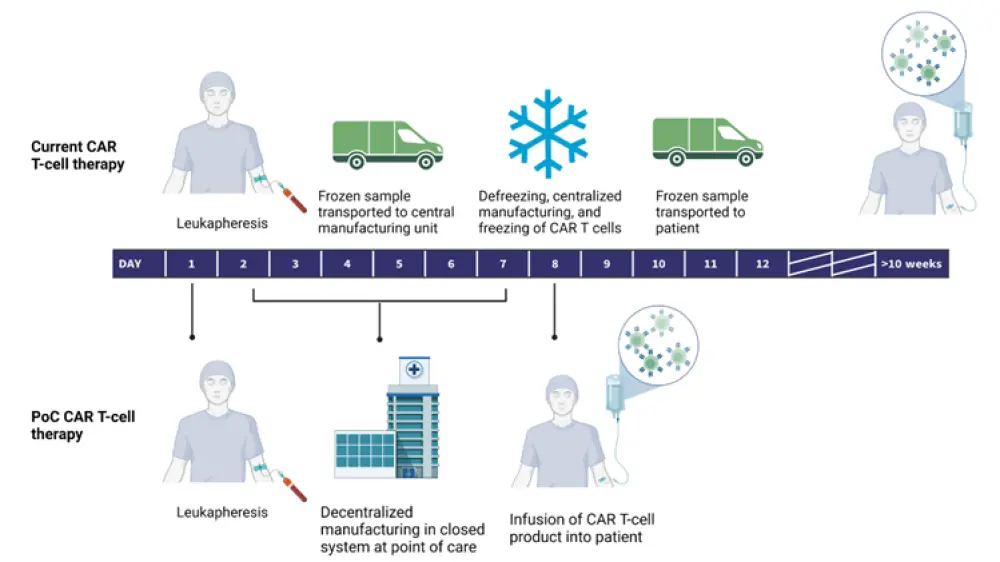
CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; PoC, point of care.
*Created with BioRender.com
Watch or download the presentation to learn more about the common challenges and solutions facing CAR T-cell therapy today, including:
- The geographical disparities in CAR T-cell funding and research
- The current progress towards, and future role of, artificial intelligence in streamlining the manufacturing process of CAR T-cell products
- The implementation of virus-free gene transfer in current genetic transposition methodologies
- In vivo CAR T-cell production using nanoparticle-encased gene transfer vectors
Key points
- Limited patient access and logistical challenges in the manufacturing of CAR T-cell products are major barriers to the wider use of these therapies.
- Access inequality to education and hands-on practice with CAR T-cell therapies between countries contributes to limited patient access.2
- The current logistical challenges disrupting the scalability and patient access to CAR T-cell therapy are:
- CAR T-cell manufacturing restricted to centralized facilities
- Acquiring clinical grade lentiviral or gammaretroviral vectors
- High cost of CAR T-cell therapy (between 253,000 and 319,000 USD per QALY)2
- Inadequate US and EU reimbursement policies1,3,4.
- Three key areas of CAR T-cell innovation are driving solutions to these challenges:
- The integration of artificial intelligence into the infrastructure of ‘smart manufacturing hospitals’ to facilitate data management and provide decision support.
- Virus-free gene transfer, to overcome the difficulties in acquiring suitable retroviral vectors.
- The simplification of CAR T-cell manufacturing using in vivo gene transfer techniques.
This activity was supported through an educational grant from Bristol Myers Squibb.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content
Your opinion matters
On average, how many patients with MGUS/smoldering MM do you see in a month?


 Michael Hudecek
Michael Hudecek

