All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the International Myeloma Foundation or HealthTree for Multiple Myeloma.
The mm Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the mm Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The mm and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Multiple Myeloma Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, Legend Biotech, Pfizer, and Roche. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View multiple myeloma content recommended for you
The impact of bridging therapy on outcomes following treatment with ide-cel in RRMM
Due to the complex nature of CAR T-cell manufacturing, which can span several weeks, bridging therapy (BT) between T-cell leukapheresis and lymphodepleting chemotherapy is often necessary. BT is vital for disease control during the CAR-T manufacturing process and to potentially reduce CAR-T-associated toxicities, decrease disease burden, and improve response durability.1
Here, we summarize a study by Afrough et al.,1 published in Blood Cancer Journal, on the impact of different BTs on outcomes in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM), treated with standard-of-care idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel).1
Study design1
- This retrospective study examined the impact of BT use and type prior to ide-cel treatment, in terms of ide-cel response and survival.
- Patients with RRMM who were being treated with ide-cel across the U.S. Myeloma Immunotherapy Consortium were included.
Key findings1
- Of the 214 patients treated with ide-cel, 170 received some form of BT.
- Overall, patients who did not receive BT experienced increased median overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) (Table 1).
- Patients receiving a BT also experienced higher rates of neutropenia and anemia than those who did not receive BT at 3 months post-infusion.
- Any-grade neutropenia: 47% vs 27.5%, respectively.
- Any-grade anemia: 79% vs 50%, respectively.
- The use of alkylators as BT was associated with the poorest OS rates, with median OS not reached, of any BT within the follow-up period (Table 1).
- Alkylators were also associated with the poorest PFS rates, despite there being no significant difference in either tumor burden or inflammatory markers at initiation.
- Response rates did not differ significantly between BT subgroups (Figure 1).
- The highest rates of immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity at Grade ≥2 were observed in patients who received selinexor BT compared with alternatives:
- Selinexor, 38%
- Alkylators, 9%
- Proteasome inhibitor combinations, 0%
- Immunomodulatory agent combinations, 17%
- Of the total cohort, 70 deaths occurred, with the most common cause being disease-related, followed by infection.
Table 1. Median progression-free survival and overall survival by bridging therapy*
|
BT, bridging therapy; IMiD, immunomodulatory agent; NR, not reached; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; PI, proteasome inhibitor. |
||||||||
|
Median survival, months |
Bridging therapy |
|
Type of bridging therapy |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
No |
|
No BT |
Selinexor |
Alkylator |
PI combo |
IMiD combo |
|
|
PFS |
6.68 |
11.48 |
|
11.48 |
9.77 |
6.51 |
6.41 |
12.01 |
|
OS |
13.85 |
NR |
|
NR |
NR |
11.97 |
NR |
NR |
Figure 1. Ide-cel response rates by bridging therapy*
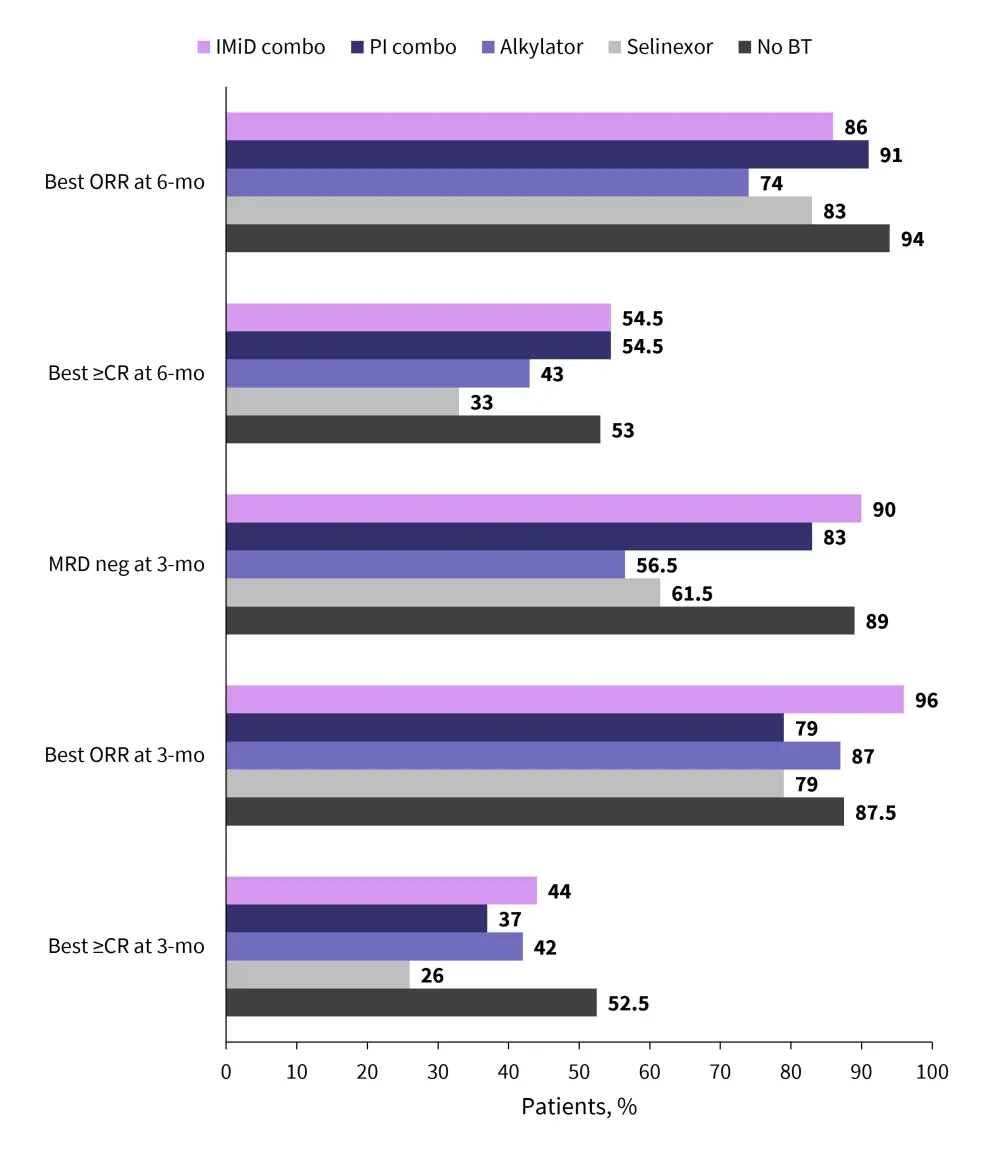
BT, bridging therapy; CR, complete response; IMiD, immunomodulatory agent; MRD, measurable residual disease; ORR, overall response rate; PI, proteasome inhibitor.
*Data from Afrough, et al.1
|
Key learnings1 |
|---|
|
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content
Your opinion matters
On average, how many patients with MGUS/smoldering MM do you see in a month?



