All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the International Myeloma Foundation or HealthTree for Multiple Myeloma.
The mm Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the mm Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The mm and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Multiple Myeloma Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, Legend Biotech, Pfizer, and Roche. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View multiple myeloma content recommended for you
U.S. FDA grants orphan drug designation to ISB 1442 for the treatment of RRMM
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted orphan drug designation to ISB 1442, a first-in-class anti-CD38/anti-CD47 bispecific antibody, for the treatment of relapsed/refractory (R/R) multiple myeloma (MM).1
ISB 14422
ISB 1442 is a biparatopic bispecific antibody with two binding arms to target CD38 and CD47. The CD47 and signal-regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) interaction is blocked by the anti-CD47 arm, whilst the anti-CD38 arm drives binding with tumor cells and through avidity-induced binding can further block adjacent CD47 receptors. ISB 1442 has an engineered fragment crystallizable region to increase antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity, antibody-dependent cell phagocytosis, and complement-dependent cytotoxicity. The structure and mechanism of action of ISB 1442 are outlined in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Mechanism of action of ISB 1442 mediated phagocytosis of tumor cells*
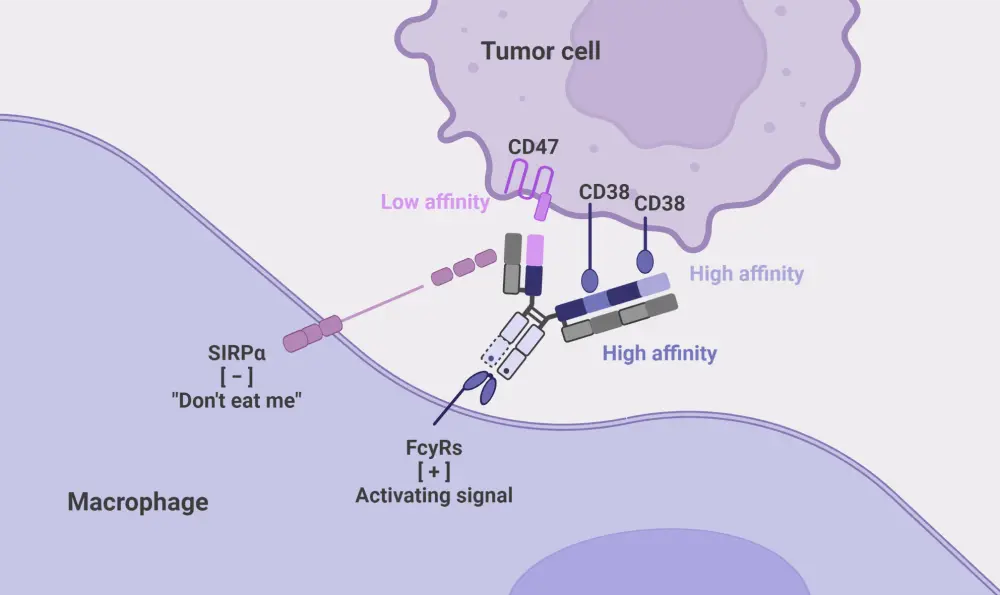
FcyRs, Fc receptors for IgG; SIRPα, signal regulatory protein α.
*Adapted from Jiang.2 Created with BioRender.com.
Preclinical data2
In comparison with daratumumab, an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, ISB 1442 demonstrated increased antitumor potency in both high and low-CD38-expressing tumors. ISB 1442 showed increased on-target tumor impacts as well as no detectable red blood cell depletion in vitro compared with magrolimab in preclinical trials.
Clinical development
An open-label, first-in-human, multicenter phase I/II study (NCT05427812) will assess the safety, tolerability, efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of ISB 1442 for R/R MM.3 Eligibility criteria include patients with R/R MM who have been treated with a CD38 antibody and have relapsed to three or more prior lines of therapy in the US.3
In this phase I trial, patients will be treated at escalating doses of ISB 1442 to establish its safety profile based on predetermined treatment-related adverse events.2 The phase II part of the trial, or dose expansion, will operate in two arms: the first being patients with three prior lines of therapy, including anti-CD38, and the second being patients who have received T cell-redirected therapies.2 The phase II primary endpoint is overall response rate. Secondary endpoints include progression-free survival, overall survival, duration of response, pharmacokinetics, and immunogenicity.2
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content
Your opinion matters
On average, how many patients with MGUS/smoldering MM do you see in a month?



