All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the International Myeloma Foundation or HealthTree for Multiple Myeloma.
The mm Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the mm Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The mm and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Multiple Myeloma Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, Legend Biotech, Pfizer, and Roche. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View multiple myeloma content recommended for you
DREAMM-2: Long-term analysis of efficacy and safety of belamaf in patients with RRMM
Do you know... In the final analysis of DREAMM-2, the overall response rate was 35% in which cohort?
Despite advances in the treatment of multiple myeloma (MM), outcomes remain poor, particularly in patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) MM. Bispecific T-cell engager monoclonal antibodies and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies have provided patients with RRMM more treatment options; however, they can be difficult to administer and are associated with considerable adverse effects. In the primary analysis and extended follow-up of the DREAMM2 trial (NCT03525678), assessing the efficacy and safety of the first-in-class B-cell maturation antigen-binding antibody (BCMA)-drug conjugate belantamab mafodotin (belamaf), durable responses were observed in heavily pretreated patients with RRMM.
Recently, Nooka et al.1 published the final analysis of the DREAMM-2 trial in Cancer. The Multiple Myeloma Hub is pleased to summarize the key findings here.
Study design
DREAMM-2 is a phase II open-label study of belamaf in patients with RRMM who had received ≥3 prior therapies. The study design and patient characteristics have previously been reported on the Multiple Myeloma Hub. For long-term follow-up, an additional independent cohort treated with 3.4 mg/kg of a belamaf lyophilized formulation was also included.
- The primary endpoint was overall response rate
- Secondary endpoints included clinical benefit rate, time-to-response, duration of response, progression-free survival, overall survival, adverse events (AEs), and ocular events
- Health-related quality of life, disease-related symptoms, and impact on functioning were also evaluated
Results
The intention-to-treat population comprised 97, 99, and 25 patients in the belamaf 2.5 mg/kg, 3.4 mg/kg, and belamaf lyophilized cohort, respectively. The data cut-off was March 31, 2022.
Efficacy
- The median follow-up was 12.5 months (range, 0.1–40.4 months), 13.8 months (range, 0.1–42.8 months), and 24.5 months (range, 1.8–38.8 months) in the 2.5 mg/kg, 3.4 mg/kg, and lyophilized cohort, respectively.
- The overall response rate was 32%, 35%, and 52% in the 2.5 mg/kg, 3.4 mg/kg, and lyophilized cohort, respectively (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Response rates*
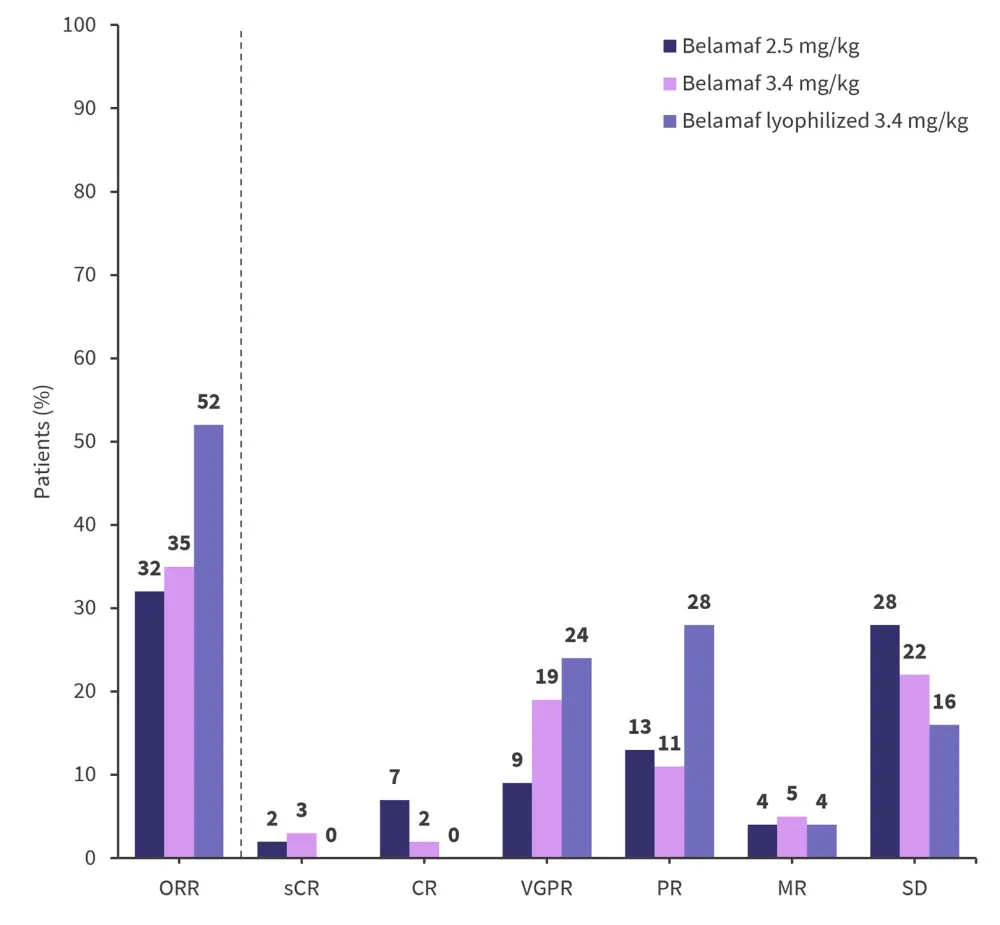
CR, complete response; MR, minimal response; ORR, overall response rate; PR, partial response; sCR, stringent complete response; SD, stable disease; VGPR, very good PR.
*Data from Nooka, et al.1
The secondary outcomes are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Secondary endpoints*
|
CBR, clinical benefit rate; CI, confidence interval; CR, complete response; DoR, duration of response; MR, minimal response; NA, not applicable; NR, not reached; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; PR, partial response; sCR, stringent complete response; TTR, time to response; VGPR, very good PR. |
|||
|
Secondary outcomes, months (95% CI; unless otherwise stated) |
Belamaf 2.5 mg/kg |
Belamaf 3.4 mg/kg |
Belamaf lyophilized 3.4 mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CBR†, % (97.5% CI) |
36.0 (26.6–46.5) |
40.0 (30.7–50.7) |
56.0 (34.9–75.6) |
|
TTR |
1.5 (1.0–2.1) |
1.4 (0.9–2.1) |
0.9 (0.8–2.3) |
|
DoR |
12.5 (4.2–19.3) |
6.2 (4.8–18.7) |
9.0 (2.8–10.4) |
|
Median PFS |
2.8 (1.6–3.6) |
3.9 (2.0–5.8) |
5.7 (2.2–9.7) |
|
Median PFS in ≥VGPR |
14.0 (9.7–NR) |
16.8 (7.7–NR) |
NA |
|
Median OS |
15.3 (9.9–18.9) |
14.0 (10.0–18.1) |
24.5 (8.7–NR) |
|
Median OS in ≥VGPR |
30.7 (19.7–37.9) |
35.5 (14.1–NR) |
NA |
|
Median duration of treatment (range), weeks |
9.3 (2.0–178.0) |
12.0 (2.0–186.0) |
16.6 (3.0–146.0) |
Safety
Rates of AEs and serious AEs (SAEs) are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Adverse events*
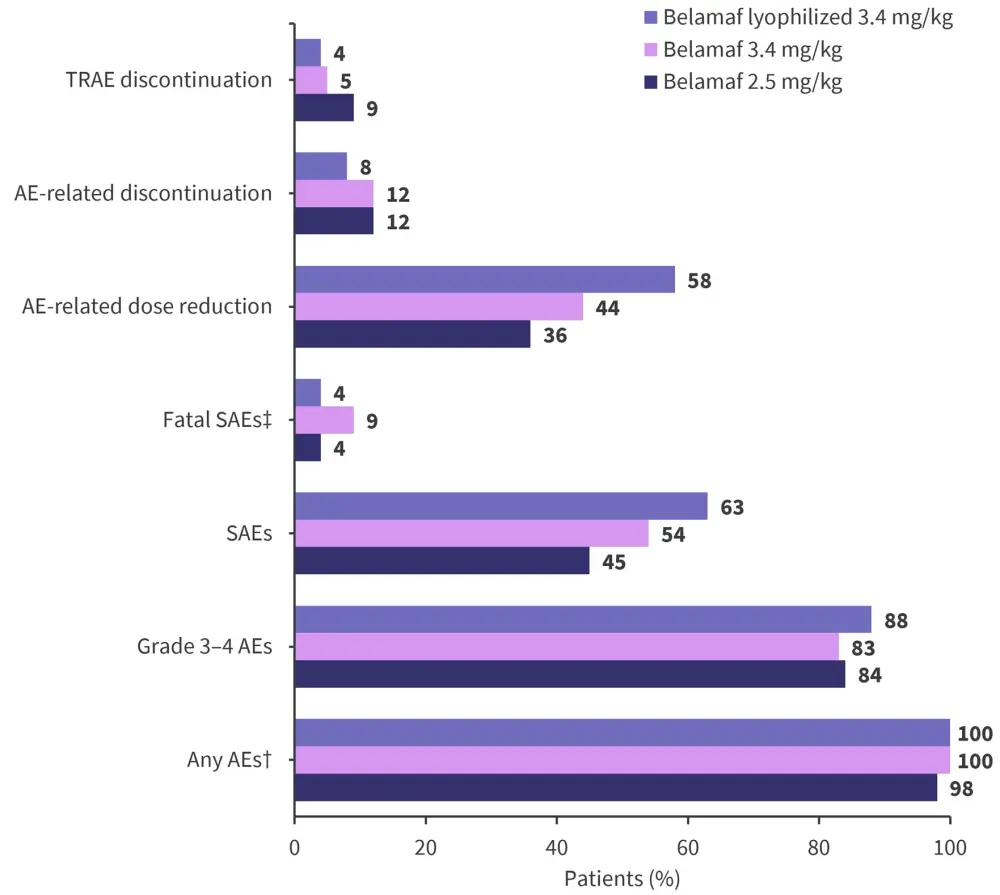
AEs, adverse events; SAEs, serious AEs; TRAEs, treatment-related AEs.
*Data from Nooka, et al.1
†AEs occurring in ≥15% of patients in the 2.5 mg/kg and 3.4 mg/kg cohorts.
‡In the 2.5 mg/kg, 3.4 mg/kg, and lyophilized cohorts, 1% (sepsis), 2% (1 cerebral hemorrhage, 1 hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis), and 0% of AEs were considered treatment related, respectively.
The most frequently reported Grade 3–4 AEs included keratopathy, thrombocytopenia, and anemia (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Grade 3–4 AEs*
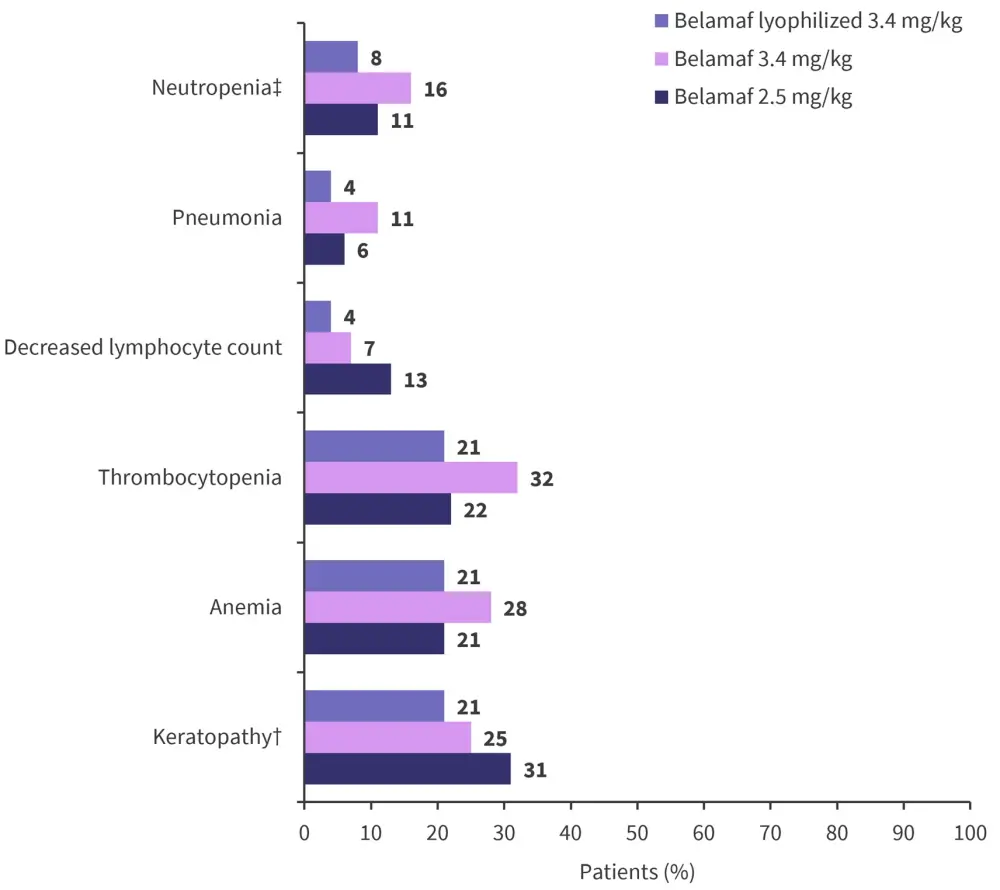
AEs, adverse events.
*Data from Nooka, et al.1
†Includes keratitis, ulcerative keratitis, infective keratitis, limbal stem cell deficiency, and punctate keratitis.
‡Includes neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, and decreased neutrophil count.
- The most frequently occurring ocular events in in the 2.5 mg/kg, 3.4 mg/kg, and lyophilized cohort, respectively, included:
- keratopathy (71%, 75%, 96%);
- blurred vision (25%, 36%, 42%);
- best corrected visual acuity reduced to 20/50 or worse (48%, 49% 75%); and
- dry eye (18%, 25%, 25%).
Patient reported outcomes
- Patients in both 2.5 and 3.4 mg/kg cohorts reported durable global health status and quality of life.
- By Week 7, there was an improvement in both fatigue and pain scores as well as disease symptoms.
- Worsening of 12.5 points in Ocular Surface Disease Index vision-related functioning was reported in 51%, 62%, and 75% of patients in the 2.5 mg/kg, 3.4 mg/kg, and lyophilized cohort, respectively.
Conclusion
The long-term analysis of the DREAMM-2 trial demonstrated deep and durable responses with belamaf at 2.5 or 3.4 mg/kg in patients with triple-class RRMM; the safety profile was also manageable. These findings are comparable with real-world studies on the benefits of belamaf and will continue to inform future studies.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content
Your opinion matters
On average, how many patients with MGUS/smoldering MM do you see in a month?



