All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the International Myeloma Foundation or HealthTree for Multiple Myeloma.
The mm Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the mm Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The mm and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Multiple Myeloma Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, Legend Biotech, Pfizer, and Roche. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View multiple myeloma content recommended for you
Epidemiological update on the incidence of multiple myeloma and mortality up to 2020
Do you know... Increased incidence of multiple myeloma in men was associated with a number of factors. Please select which factor was not found to be associated with the incidence of MM in men:
Introduction
Multiple myeloma (MM) was the third most prevalent hematologic malignancy in 2020. As many previous studies were restricted in terms of the number of countries included or used relatively old data, an updated epidemiological review of the global incidence of novel MM cases and mortality is needed. This is especially important following the advent of new therapeutic agents and transplantation strategies, which have more than doubled (54%) the 5-year overall survival rate for patients with MM.
A study by Junjie Huang, et al.,1 published in Lancet Hematology investigated global trends in MM and the associated lifestyle factors and metabolic risk factors.
For 2020, the study reported:
- an estimated 176,404 (95% uncertainty interval [UI], 167,933–185,303) new cases of MM and 117,077 (95% UI, 109,930–124,689) deaths worldwide; and
- an age standardized rate of MM incidence of 1.78 (95% UI, 1.69–1.87) per 100,000 people and mortality of 1.14 (95% UI, 1.07–1.21) per 100,000, worldwide.
Study design
Multiple databases were used to conduct this study, including:
- The Global Cancer Observatory (GLOBOCAN) database was used for the number of new cases, deaths, incidence and mortality in 2020
- World Health Organization (WHO) Global Health Observatory (GHO) database provided information on lifestyle factors
- The United Nations (UN) repository was used for human development index (HDI) data
- For trend analysis and to obtain MM incidence and mortality between 1980−2019:
- the Cancer Incidence in Five Continents Time Trends (CI5plus);
- the WHO mortality database;
- the Nordic Cancer Registries (NORDCAN); and
- the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program (SEER) were used.
Results
Global incidence of newly reported cases of MM and MM-associated mortality
Figure 1A shows the countries with the highest and lowest incidence of MM. The top three countries in terms of incidence all have a high HDI. There was a difference in incidence between men and women, with men having a 47% higher incidence rate than women (2.10 [95% UI, 1.97–2.25] vs 1.47 [95% UI, 1.36–1.58]).
Figure 1B shows the newly reported global MM-associated deaths in 2020, which were estimated to be 117,077 worldwide. Polynesia showed the highest mortality rate overall, whereas Micronesia showed the lowest. Higher HDI was associated with a higher MM-associated death rate.
Figure 1A and B. Countries with the highest and lowest incidence of new cases A and newly-reported MM deaths B in 2020*
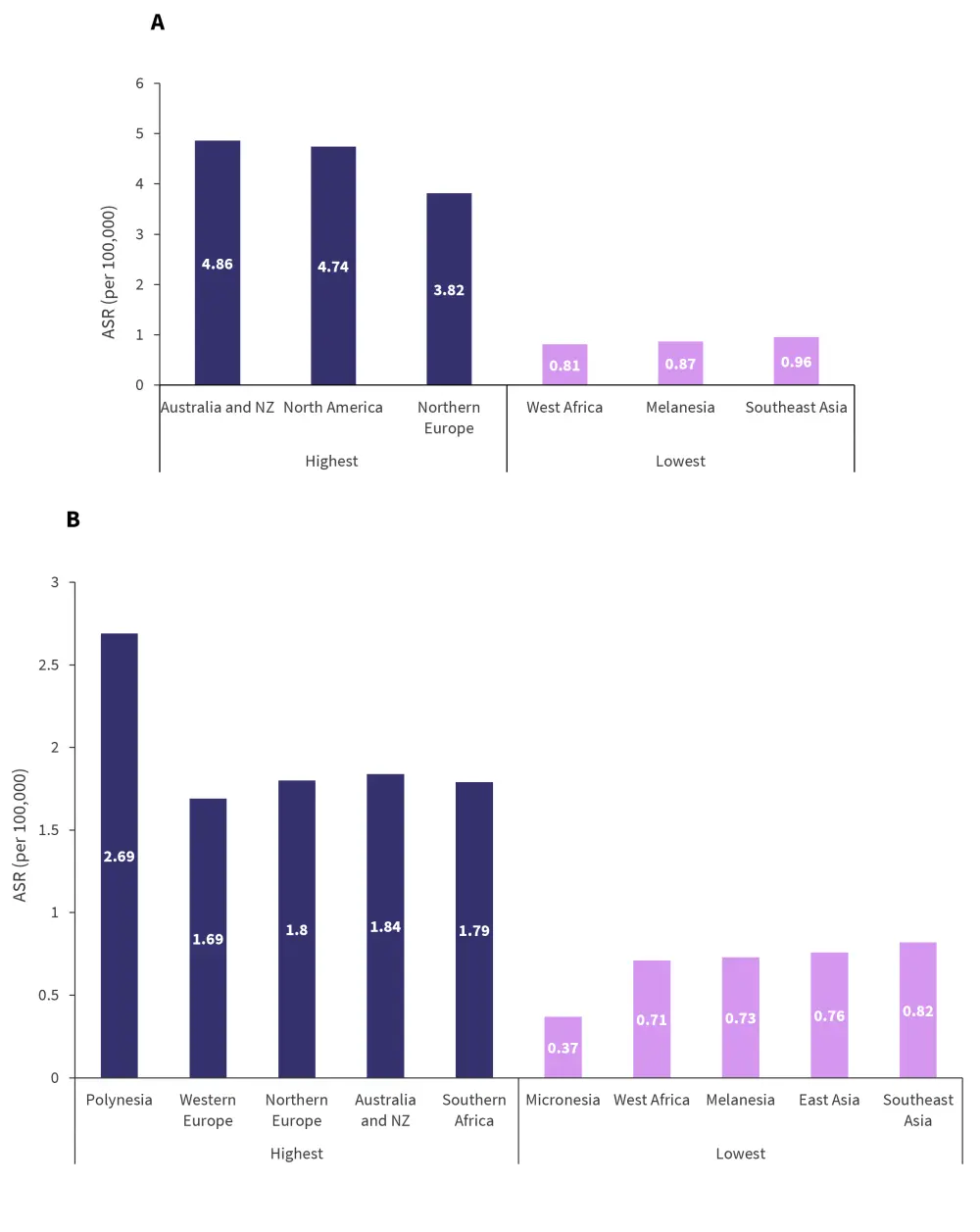
ASR, age-standardized rate; NZ, New Zealand; MM, multiple myeloma.
*Adapted from Huang, et al.1
Association of MM incidence and mortality with lifestyle factors
In male patients, an increased MM incidence was associated with:
- higher gross domestic product (GDP) per capita (β [degree of change in ASR of incidence or mortality of multiple myeloma per unit increase in the factors examined] 0.26; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.13–0.39]; p < 0.0001);
- HDI (0.32; 95% CI, 0.15–0.49]; p = 0.00027); and
- a lower prevalence of smoking (−0.02; 95% CI, −0.04 to −0.003; p = 0.026).
In female patients, an increased MM incidence was associated with:
- a higher GDP per capita (0.14; 95% CI, 0.04–0.24; p = 0.0048);
- higher HDI (0.22; 95% CI, 0.09–0.35; p = 0.0012);
- higher prevalence of physical inactivity (0.01; 95% CI, 0.0004–0.03; p = 0.043);
- being overweight (0.01; 95% CI, 0.002–0.03; p = 0.025); and
- and obesity (0.02; 95% CI, 0.006–0.04; p = 0.0076).
With respect to MM-associated deaths, a higher mortality rate in men was associated with a higher HDI (β, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.09–0.30; p = 0.00028). In women, a higher mortality rate was also associated with a higher HDI (0.13; 95% CI, 0.05–0.22; p = 0.0026) and higher prevalence of physical inactivity (0.01; 95% CI, 0.004–0.02; p = 0.0047), being overweight (0.01; 95% CI, 0.004–0.02; p = 0.0018), obesity (0.02 95% CI, 0.009–0.03; p = 0.00024), and diabetes (0.03; 95% CI, 0.007–0.06; p = 0.013).
Assessment of the countries with available data (48) showed an overall increasing trend in MM incidence, particularly in men, people aged ≥50 years, and in high-income countries. In contrast, there was a decreased trend for MM-associated mortality, although this was less prevalent in male patients compared with female.
Differences in incidence and MM-associated mortality between sexes
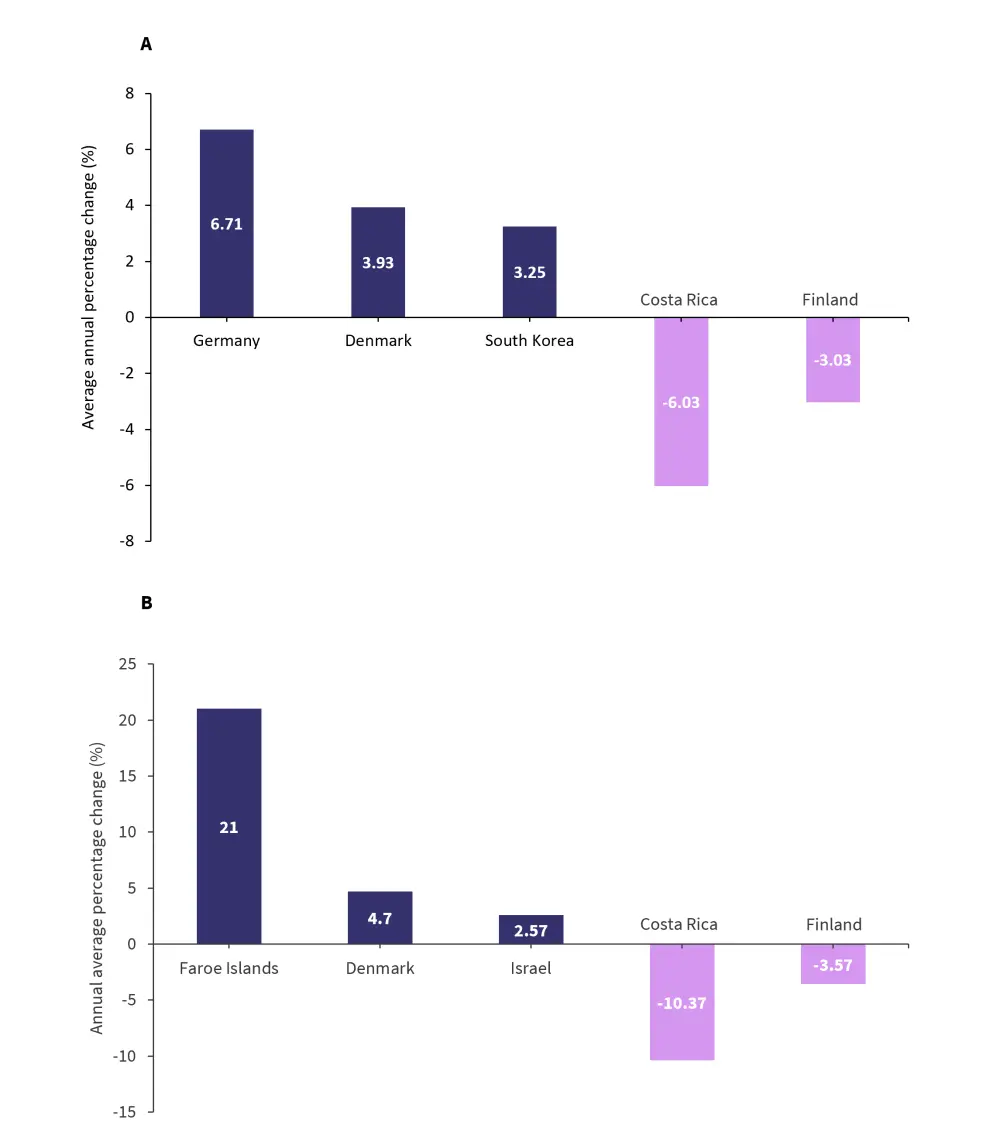
Countries in which the incidence of MM significantly increased or decreased in female and male patients is shown in Figure 2A and B, respectively. The countries which showed the greatest significant increases in incidence were in Europe for both sexes.
Figure 2A and B. Countries reporting a significant change in incidence of MM in women A and men B from 2001–2019*
MM, multiple myeloma.
*Adapted from Huang, et al.1
Mortality associated with MM in men was significantly increased in seven countries (Figure 3A), with Thailand showing the highest significant average annual percentage change (AAPC) at 40.82%; this was over six times higher than the second highest, Ecuador. Thailand also was the country that showed the greatest increase in women (AAPC, 47.37%), followed by Latvia (Figure 3B). The authors noted that these must be analyzed with respect to the baseline mortality rates to enable a comprehensive assessment of trends.
Figure 3A and B. Countries reporting a significant change MM-associated mortality in men A and women B from 2001–2019*
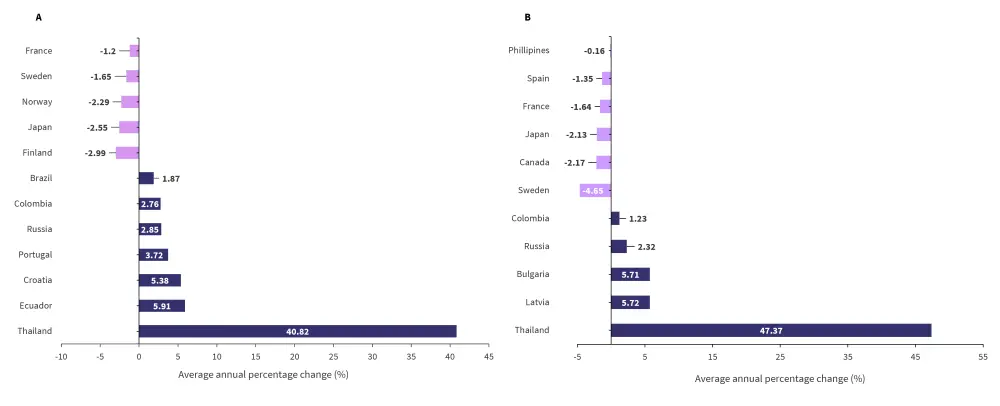
MM, multiple myeloma.
*Adapted from Huang, et al.1
Association between age, MM incidence, and MM-associated mortality
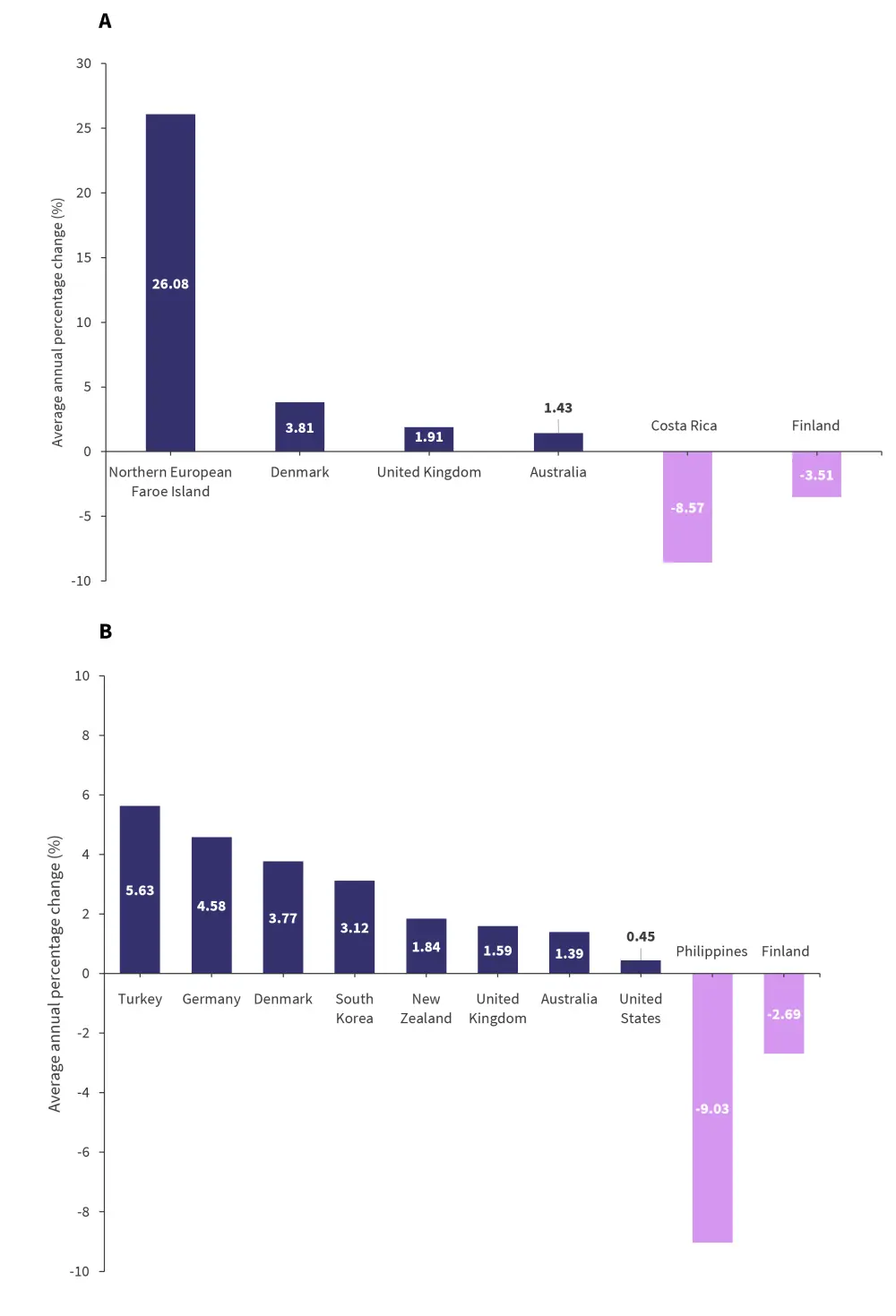
In patients aged > 50 years, the top three countries that showed a significant increase in AAPC are shown in Figure 4A. Only two countries, Finland, and Costa Rica, showed a significant decrease in the incidence of MM in male patients aged >50 years old. For men aged <50 years, only Iceland reported a significant increase (14.54; 95% CI, 11.33–17.85; p < 0.0001), and no country reported a decrease.
In female patients aged >50 years old, the Faroe Islands showed the largest significant increase in AAPC. Costa Rica and Finland were the only countries that showed a significant decrease in AAPC for women aged >50 years (Figure 4B). There were four countries that reported a significant increase in incidence of MM in women < 50 years old including
- South Korea (9.56; 95% CI, 2.49–17.12; p = 0.013);
- the UK (6.22; 95% CI, 3.99–8.50; p = 0.00018); and
- the USA (4.07; 95% CI, 1.53–6.69; p = 0.0059).
No country reported a decrease in MM incidence in women aged <50 years.
Figure 4A and B. Incidence of MM in male A and female B patients aged >50 years*
MM, multiple myeloma.
*Adapted from Huang, et al.1
Limitations
This study had several limitations, such as a failure to account for the effect of COVID-19 pandemic on estimates of the GLOBOCAN 2020 database. Diabetes prevalence did not differentiate between patients with type 1 and type 2, as this data was not available. In countries with under-developed cancer reporting mechanisms, it may be possible that the incidence and mortality of MM is inaccurate. Also, in some countries with cancer registries in major cities, figures may have been overestimated.
Conclusion
These results highlight the wide disparity in the burden of MM between different countries regarding both incidence and mortality. An association was noted between higher HDI and male sex and a higher mortality and incidence of MM. Certain preventable lifestyle factors were shown to be associated with an increased incidence and mortality in patients with MM such as, diabetes, reduced physical activity, being overweight, and obesity. Patients from higher-income countries, who are male or aged >50 years, showed a higher incidence of MM. Overall, there was a trend of decreasing mortality associated with MM worldwide over time, with this trend being particularly apparent in women.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content
Your opinion matters
On average, how many patients with MGUS/smoldering MM do you see in a month?

